April 13, 2023
2867
Vacuum tube and transistor are both electronic components used a variety of electronic devices and circuits such as computers, communication systems, TV, radios, amplifiers and others. However, both are significantly different from each other based on their technology and operation. Let's dive in it and reveal the truth of them.
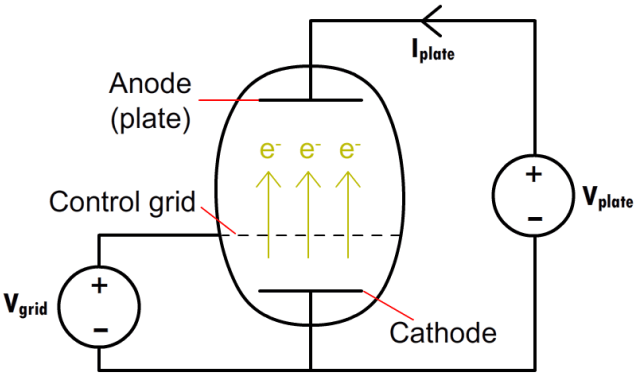
Vacuum Tube" stands for a vacuum inside the glass bottle to facilitate the flow of free electrons and to effectively reduce oxidation losses in the filament. Similar to transistors, they can be two-pole, three-pole, five-pole, etc. Also known in "audiophile" circles as "bile tubes".
Due to the disadvantage of it, such as larger, fragile like a light bulb, and expensive, the invention of the transistor started to replace the vacuum tube. As computing devices started to become smaller in size, transistors were more ideal to use due to their smaller size. However, Vacuum tubes still have some advantages over transistors, such as their ability to handle high voltages and currents, and their warm and pleasant sound in audio amplification applications.
Today, vacuum tubes are primarily used in high-end audio equipment, preferred by some audiophiles as an alternative to digital systems.
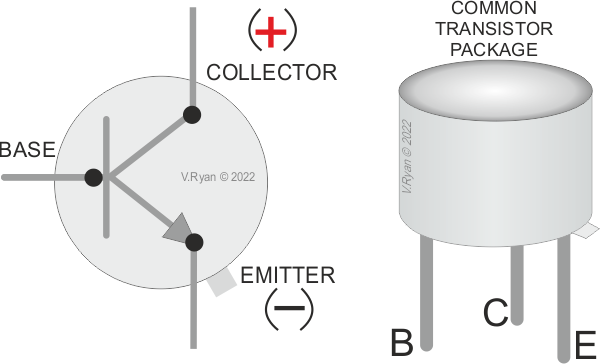
A transistor is a semiconductor device that controls the flow of current between two terminals. As a variable switch, the transistor controls the outgoing current based on the input voltage, so the transistor can be used as a current switch. Transistors are used in second generation computers.
The transistor consists of three parts, the base, the collector and the emitter. When a voltage is applied to the base-collector terminal, electrons move from the base to the collector. To control the amount of current flowing from the base to the emitter, a resistor is connected in series with the base-emitter junction.
Vacuum tubes are electronic devices that amplify sound or other electrical signals. They were once widely used in radios and televisions. They are much smaller and more efficient. Compared to transistors, vacuum tubes are bulky and inefficient. They also require high voltage and heat to work properly. Key differences between a vacuum tube and a transistor as the chart below:
differences | Vacuum Tube | Transistor |
Physical size and power consumption | Larger in size | solid-state devices |
Reliability and lifespan | shorter lifespan | a longer lifespan. |
Efficiency and heat dissipation | higher internal | more efficient and dissipate less heat |
Linearity and distortion | warm smooth natural sound | clean accurate linear sound |
Cost and availability | more expensive and less available | relatively inexpensive and widely available |
Vacuum Tubes | Transistors |
Audio Amplification
| Amplification
|
Radio Communication
| Switching
|
Industrial Heating
| Oscillation
|
X-ray Generation
| Voltage regulation
|
Scientific Research
| Temperature sensing
|
Application requirements - Consider the specific requirements of your electronic project, such as the desired frequency range, power output, voltage range, and temperature range.
Availability and cost – Consider your budget of electronic components, whether it is a vacuum tube or a transistor. Choose the right one depending on the special use.
Size and power consumption - If your project requires a small and low-power device, a transistor may be more suitable while a vacuum tube suits for large and high-power device.
Reliability and lifespan - Some components may have a longer lifespan or higher reliability than others, so choose the component that meets your requirements for stability and longevity.
Personal preference - If you are more familiar with one type of component over another, or have a personal preference for one type, then choose the component that you feel most comfortable working with.
Both vacuum tubes and transistors have their strengths and weaknesses, and both have their own unique characteristics that make them suitable for different applications.