January 25, 2024
3538
The semiconductor industry has witnessed a transformative shift with the emergence of fabless semiconductor companies. In this innovative business model, companies focus on semiconductor design and intellectual property (IP) development while outsourcing the manufacturing process to external foundries. This separation of design and manufacturing responsibilities allows for greater flexibility and efficiency in bringing cutting-edge semiconductor products to market. In this article, we explore the concept of fabless semiconductor companies, their advantages, and a list of top players in the industry.
In a fabless semiconductor model, a company focuses on the design and sale of semiconductor chips but does not have its own manufacturing facilities for producing the silicon wafers or chips. Instead, it relies on outsourcing the fabrication process to external manufacturing plants or foundries. This allows the company to concentrate on innovation, design, and marketing without the need for extensive investment in semiconductor manufacturing infrastructure. The term "fabless" essentially highlights the separation of chip design and manufacturing responsibilities in the semiconductor industry.
A fabless company in the semiconductor industry refers to an enterprise model where the company develops and owns intellectual property (IP) related to semiconductor technology but outsources the actual manufacturing of semiconductor chips. In this model, the company focuses on semiconductor design, innovation, and the development of intellectual property without the need to have its own manufacturing facilities.
Typically, these companies delegate the manufacturing tasks of the designed semiconductor chips to third-party manufacturing plants or foundries. These manufacturing facilities are responsible for using their production equipment and expertise to manufacture the chips based on the design files provided by the company. Once the chips are fabricated, they are sent back to the fabless company for testing, packaging, and eventual product distribution.
The choice of this model allows fabless semiconductor companies to concentrate on innovation and design while avoiding significant capital investments in semiconductor manufacturing infrastructure. This flexibility enables these companies to rapidly introduce new products and better adapt to market demands and technological advancements.
Fabless manufacturing is a business model in the semiconductor industry where a company focuses on designing and marketing semiconductor chips but does not engage in the actual manufacturing (fabrication) of the chips. Instead of owning and operating its own semiconductor fabrication facilities, a fabless company outsources the manufacturing process to third-party foundries or manufacturing plants.
Fabless manufacturing allows companies to specialize in chip design and innovation without the significant capital investment required for semiconductor fabrication facilities. This business model is prevalent in the semiconductor industry, and many well-known companies operate as fabless semiconductor firms.
Headquarters: United States
Revenue (2020): $19,407 million USD
Description: Qualcomm is a global leader in wireless communication technologies and semiconductor solutions. The company is known for its advancements in mobile processors, wireless communication technologies, and contributions to the development of 5G technology.
Headquarters: United States
Revenue (2020): $17,745 million USD
Description: Broadcom is a diversified semiconductor company with a focus on designing and providing a broad range of semiconductor and infrastructure software solutions. The company's products are widely used in networking, storage, broadband, wireless, and industrial applications.
Headquarters: United States
Revenue (2020): $15,412 million USD
Description: Nvidia is renowned for its graphics processing units (GPUs) and AI-driven computing technologies. The company's GPUs are widely used in gaming, professional visualization, data centers, and automotive markets. Nvidia has been a key player in the development of GPU-accelerated computing.
Headquarters: Taiwan
Revenue (2020): $10,929 million USD
Description: MediaTek is a Taiwanese fabless semiconductor company specializing in the design of chipsets for a variety of electronic devices. The company's products include processors for smartphones, smart TVs, wearable devices, and home entertainment systems.
Headquarters: United States
Revenue (2020): $9,763 million USD
Description: AMD is a major player in the semiconductor industry, particularly known for its CPUs and GPUs. The company's processors are used in desktops, laptops, servers, and gaming consoles. AMD has been competitive in challenging Intel's dominance in the CPU market and has made significant strides in the GPU market.
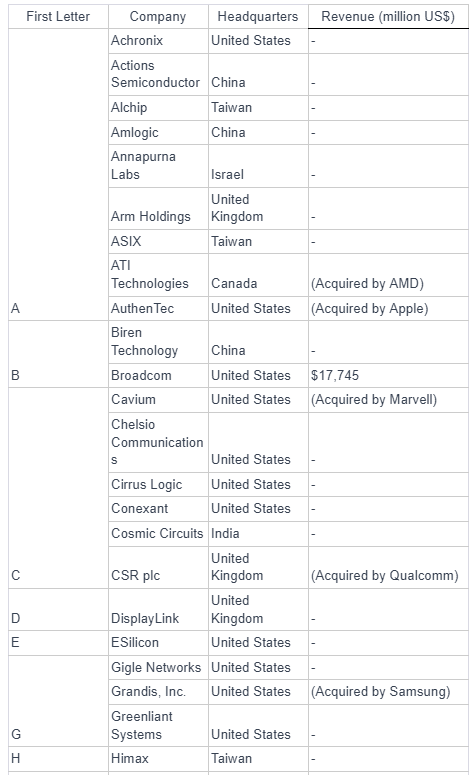
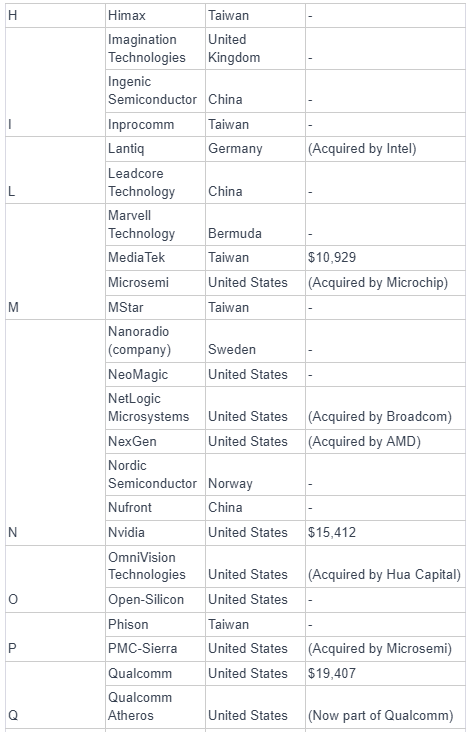
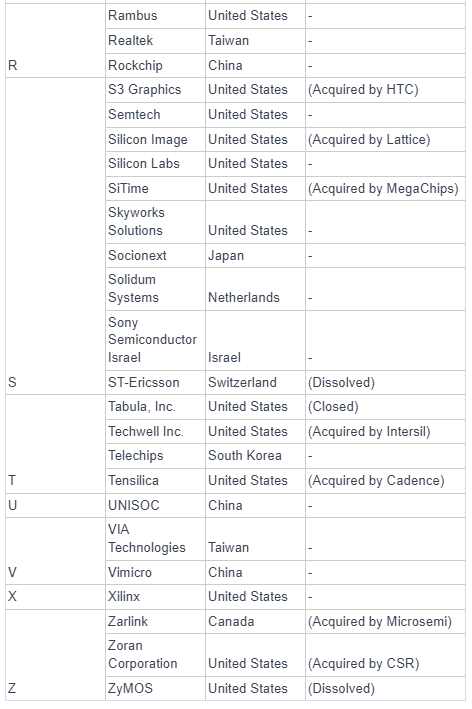
As of the second half of 2023, Nvidia emerged as the world's largest fabless semiconductor company, surpassing Qualcomm, at least temporarily. The rankings of the largest fabless semiconductor companies can be dynamic and subject to change based on various factors, including market trends, product innovations, and financial performance.
The terms "semiconductor fab" and "fabless" represent two distinct approaches in the semiconductor industry, each emphasizing different aspects of the semiconductor manufacturing process. In summary, the key distinction lies in whether a company owns and operates its semiconductor fabrication facilities (semiconductor fab) or outsources the manufacturing process while focusing on design (fabless).
A semiconductor fab, short for fabrication facility, refers to a manufacturing plant where semiconductor devices or chips are produced.
Manufacturing Focus: Semiconductor fabs are equipped with cleanrooms and specialized equipment for the fabrication process. This process involves creating integrated circuits on silicon wafers through techniques like photolithography, etching, doping, and metallization.
Ownership: Companies that operate semiconductor fabs own and manage the entire manufacturing process in-house. They invest in the infrastructure, equipment, and expertise required for chip fabrication.
Examples: Companies like Intel, Samsung, TSMC (Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company), and GlobalFoundries are known for owning and operating semiconductor fabs.
Fabless companies, on the other hand, focus on designing semiconductor chips rather than manufacturing them. The term "fabless" is a combination of "fabrication" and "less," indicating the lack of in-house fabrication facilities.
Design Focus: Fabless companies specialize in chip design, including creating the architecture, functionality, and specifications of semiconductor devices. They focus on innovation, research, and development of intellectual property (IP).
Outsourcing Manufacturing: Instead of investing in semiconductor fabs, fabless companies outsource the actual manufacturing (fabrication) of their designed chips to third-party foundries or manufacturing facilities. This allows them to leverage the expertise and infrastructure of established manufacturing plants.
Examples: Nvidia, Qualcomm, AMD (Advanced Micro Devices), and MediaTek are prominent examples of fabless semiconductor companies.
Ownership and Control
Semiconductor fabs own and control the entire manufacturing process, from design to fabrication. Fabless companies, on the other hand, focus solely on design and outsource fabrication to external facilities.
Investment and Expertise
Semiconductor fabs require substantial investments in manufacturing infrastructure, cleanrooms, and equipment. Fabless companies can allocate resources primarily to design and innovation without the need for extensive manufacturing expertise.
Flexibility
Fabless companies enjoy greater flexibility as they can adapt quickly to changes in technology and market demands without being tied to a specific manufacturing facility.
In 1985, a transformative shift occurred in the semiconductor industry with the founding of Chips and Technologies by Dado Banatao and Gordon Campbell. This marked the inception of the first fabless semiconductor company, pioneering a business model that would significantly influence the industry's trajectory. Chips and Technologies departed from the traditional integrated device manufacturing (IDM) model by exclusively focusing on chip design and relinquishing the need for in-house manufacturing facilities.
The innovative approach of Chips and Technologies, under the leadership of Banatao and Campbell, introduced a level of flexibility previously unseen in semiconductor companies. By adopting the fabless model, the company could concentrate on chip design, innovation, and intellectual property (IP) development, while outsourcing the fabrication process to external semiconductor foundries. This newfound agility allowed for swift adaptation to market demands and technological advancements, setting a precedent for the industry.
The impact of Chips and Technologies on the semiconductor sector was profound. As the first successful fabless semiconductor company, it catalyzed a broader industry transformation. Numerous companies followed suit, embracing the fabless approach as a viable and efficient means to bring semiconductor products to market. Silicon Valley, already a hub of technological innovation, witnessed the rise of a new wave of companies influenced by the success and ethos of Chips and Technologies.
The legacy of Chips and Technologies extends beyond its pioneering role. The fabless semiconductor model it championed has become a dominant and enduring paradigm in the industry. Today, many leading semiconductor companies operate as fabless entities, emphasizing design and innovation while outsourcing manufacturing. Chips and Technologies, through its groundbreaking business model, not only shaped the industry landscape but also contributed to the dynamic and collaborative environment of Silicon Valley, leaving an indelible mark on the evolution of semiconductor technologies.
While the fabless semiconductor business model offers advantages such as cost efficiency and flexibility, it also comes with certain disadvantages that companies operating in this mode need to navigate.
Supplier Reliance
Fabless companies heavily rely on external foundries for the fabrication of their semiconductor products. If a foundry decides to stop producing chips or raises its prices, fabless companies may face significant challenges. The sudden unavailability or increased costs of fabrication services can disrupt production schedules and impact the company's ability to meet market demands.
Supply Chain Risks
Fabless companies are susceptible to supply chain vulnerabilities. Changes in the foundry's operational status, technological capabilities, or geopolitical factors can introduce uncertainties. A sudden shift in the foundry landscape, such as closures or capacity constraints, poses risks to the fabless semiconductor companies relying on these external manufacturing partners.
Limited Control Over Fabrication
Fabless companies relinquish direct control over the fabrication process when outsourcing to external foundries. This lack of control can lead to challenges in maintaining consistent product quality. Variabilities in manufacturing processes, equipment, or materials at the foundry may impact the final product's performance and reliability.
Quality Assurance Complexity
Ensuring the quality of semiconductor products becomes more complex when production is outsourced. Fabless companies must implement robust quality assurance and testing procedures to mitigate potential issues. Variations in manufacturing processes across different foundries may require additional efforts to maintain standardized quality levels.
These disadvantages are inherent to the fabless model but are often managed through strategic supplier relationships, diversified sourcing strategies, and stringent quality control measures. Fabless companies mitigate risks by collaborating closely with foundries, diversifying their manufacturing sources, and staying abreast of industry trends. While the fabless model offers flexibility and cost advantages, it requires effective risk management strategies to navigate challenges related to supplier dependencies and quality control.
The world of fabless semiconductor companies represents a dynamic and efficient approach to semiconductor innovation. By concentrating on design and outsourcing manufacturing, these companies navigate the complex landscape of semiconductor production. While the fabless model offers advantages such as flexibility and cost efficiency, it also poses challenges, particularly in dependency on foundries and quality control. Nevertheless, the legacy of pioneers like Chips and Technologies, the first fabless semiconductor company, continues to shape the industry's trajectory. As technology advances and market dynamics evolve, fabless semiconductor companies remain pivotal players in the ever-expanding semiconductor ecosystem.