Published :11/12/2019 8:43:58 PM
Click Count:2103
Books are perishable, photos will eventually fade, CDs and hard drives will last for years, so are there better data storage media? Microsoft has found a new way to store data. The company worked with Warner Bros. to store the 1978 version of Superman in a piece of glass with up to 75.6GB of data. This is the practice of glass hard disk from concept to landing.
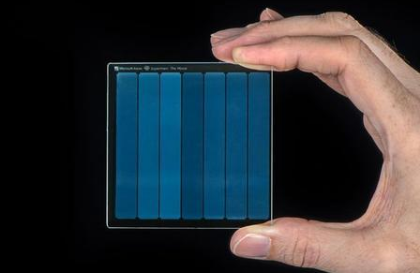
p style="text-indent: 2em;">This glass is the coaster size, 75 mm x 75 mm x 2 mm. Microsoft uses infrared laser to decode movie data into three-dimensional pixels. After storing it in glass, the data can be read and decoded by machine learning. Unlike digital hard disk storage, glass hard disks are laser-encoded by creating a layer of three-dimensional nano-gratings and distortions at different depths and angles of the glass. Reading data requires a machine learning algorithm to decode the polarized light through the glass. Generated images and patterns.The principle of encoding and decoding is that a femtosecond laser (a LASIK procedure that emits ultrashort pulses of light and is commonly used to treat myopia) melts the glass to form a nano-grating associated with light polarization. Structure, then the point written to the nano-grating can represent "1", while "0" does not need to be written. Previously, Associate Professor James Chon and Professor Gu Min from the Swinburne University of Science in Australia implemented data storage in 2009, which is to achieve information coding in five dimensions, including polarization, wavelength and x, y of light. z 5 physical dimensions such as three coordinates.
Warner Bros. converts the digital copy back to analog film and divides it into 3 color components (cyan, magenta, and yellow) to transfer it to the black and white film negative. It won't fade like color film. Microsoft said that a 2 mm thick glass can contain more than 100 data layers. Each layer consists of a laser-written nano-grating, and then a machine learning algorithm jumps between them to decode it.
For a long time, Warner Bros. has been looking for long-term storage of "cold" data that does not require frequent access. The company currently uses film to store huge amounts of video data in a temperature and humidity controlled cold storage. From time to time, detectors are used to detect chemical decomposition. The solid state drives that store digital files need to be migrated every 3 years. Avoid electronic attenuation and lose data.
This process is costly. Warner Bros. has also made a number of preparations to guard against data storage incidents, such as dealing with earthquakes or hurricanes, and preventing fires and floods from damaging film. They are prepared to place 3 copies around the world, 2 copies of the digital copy, and 1 copy of the original material. Microsoft's silicon project allows them to see the hope of storing data once and for all.
Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella said the glass hard drive system is a brand new cold storage system. It is important to know that glass is boiled, baked and scratched without compromising its storage stability, so the data can be stored for centuries. In addition, glass storage does not require temperature and humidity control, which greatly reduces the environmental cost of the database. Glass hard drives are more fidelity. Warner Bros. file executive Brad Collar said that today's filming is digital, and digital pixels need to be stored in film analog media, which loses the original pixels, and this is irreversible, while glass storage is like a camera. The original pixel.
Glass hard drives also have a big advantage over CDs. CD discs can only store "0", "1" with bumps on the plane, and glass can be stored in a three-dimensional array for high storage density. Laser technology can store 100 multi-layer three-bit pixels in 2 mm glass. In addition, glass storage accesses data through optical readers at a faster rate. Machine learning algorithms can quickly locate data and then homing, greatly reducing the delay in extracting information, while optical discs and tapes take time to find the read position.
Microsoft's project is called the Silicon Project, and Microsoft Research is the responsible department. As a technology giant, Microsoft hopes that glass hard drives will meet the long-term storage needs of data. Glass storage research was conducted by Microsoft in collaboration with the University of Southampton in the UK, which developed a technology for storing data in glass using femtosecond technology in 2013.
Glass is still a bit special, because Microsoft's technology is a change in the physical properties of glass under laser illumination, especially when using pulsed lasers with multiple pulses. The distribution of such periodic nanogratings is formed within. This periodic nano-grating structure associated with polarization orientation is the principle of its storage. If there is no such mechanism for switching to other substances, there is no way to achieve multiplexing of polarization dimensions. At the same time, the glass has the characteristics of high temperature resistance, electromagnetic interference resistance and wear resistance, so it can be stored for several thousand years.
Cold data is also worth saving. For example, the WeChat of your circle of friends is sent out. Maybe a friend visits and clicks a lot on the same day or within a week, but the data is no longer accessed after one week, but according to national laws, the data is useful and effective. The company is obliged to keep this information. Big data now stores a lot of data every day, but if you don't save it, it's a pity, but if you want to save it all, the storage medium is not enough.
The advantage of Microsoft's glass is that the material is relatively simple, but they have the biggest problem, that is, the technical principle determines that it is not fast enough because it requires multiple pulse writes. Data, so staying at each point takes a long time. The method we use solves the problem of their writing speed, and can record a single pulse, so it is 1 to 2 orders of magnitude faster than Microsoft's technology! Moreover, we can achieve multiplexed storage for 7 dimensions, and storage capacity is 2 to 3 orders of magnitude higher than Microsoft's technology.