Published :2/2/2021 4:22:10 AM
Click Count:2103
NXP’s total revenue in the fourth quarter of 2020 was US$2.5 billion, a year-on-year increase of 9%; net profit was US$320 million, a year-on-year increase of 160%; basic earnings per share were US$1.1, and earnings per share in the same period last year were US$0.41.
The total revenue for the whole year of 2020 was US$8.6 billion, down 3% year-on-year; net profit was US$80 million, down 71% year-on-year; basic earnings per share were US$0.19, and earnings per share in the same period last year were US$0.86.
The operating cash flow for the year was US$2.482 billion, and the net capital expenditure investment was US$388 million. NXP approved the payment of an interim dividend of US$0.375 per share in the fourth quarter of 2020; in 2020, the company returned US$1.047 billion to shareholders through the previously announced share repurchase program and dividend payment.
Looking ahead, NXP expects total GAAP revenue in the first quarter of 2021 to be US$2.48 billion to US$2.63 billion, an increase of 22%-30% year-on-year; GAAP gross profit margin is expected to increase from 51.8% to 52.5% year-on-year; operating profit is 468 million to 543 million US dollars.
NXP was formerly the semiconductor business of Philips. It was separated into an independent company in 2006 and listed on the Nasdaq Stock Exchange in August 2010. After NXP acquired Freescale Semiconductor in the United States in December 2015, it has gradually become a leader in the automotive semiconductor and general-purpose microcontroller market.
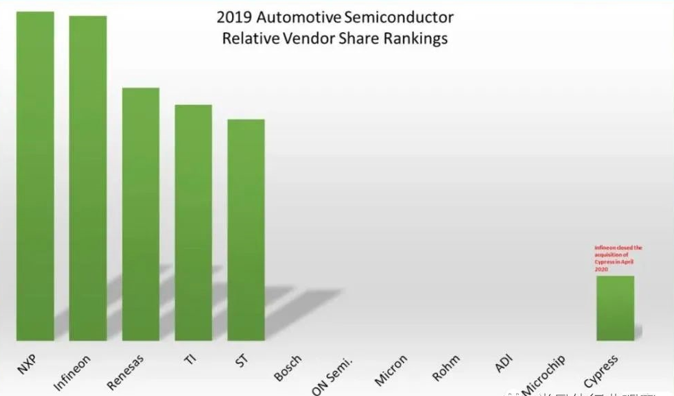
At the same time, the automotive business has also become NXP's main source of revenue. In 2019, the company's total revenue reached US$8.877 billion. Among them, revenue from automobiles accounted for 47%, and revenue from industry and the Internet of Things, mobile devices, communication infrastructure and others were 18%, 13%, and 21%.
In addition, in 2019, more than half of NXP's revenue came from China and the Asia-Pacific region except Japan and South Korea, 20% of its revenue came from EMEA, the Americas and Japan each accounted for about 10%, and South Korea less than 5%. It can be seen that the contribution of the Chinese market to NXP has taken a pivotal position.
For NXP, the growth rate of the automotive business depends on global automotive production and sales, as well as the degree of application of semiconductor equipment in automobiles, that is, the degree of electronics. NXP said in its 2019 annual report that the decline in automotive business revenue was mainly due to the decline in automobile production and sales in China and other countries in the Asia-Pacific region, and this decline is also gradually in EMEA (Note: Europe, Middle East and Africa) and the Americas. appear.
China has created a huge source of revenue for NXP, but at the same time NXP has also brought another dimension of contribution to Chinese semiconductors.